 The SouthEast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) project, SouthEast Alaska Tribal Toxins (SEATT) partnership and the Sitka Tribe of Alaska Environmental Research Lab (STAERL) have expanded a recent paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) advisory to include more beaches in Southeast Alaska.
The SouthEast Alaska Tribal Ocean Research (SEATOR) project, SouthEast Alaska Tribal Toxins (SEATT) partnership and the Sitka Tribe of Alaska Environmental Research Lab (STAERL) have expanded a recent paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) advisory to include more beaches in Southeast Alaska.
The advisory, initially announced on May 26, now includes multiple beaches in Sitka, Juneau, Craig, Petersburg, and Klawock. The PSP advisory is for bivalve shellfish — such as clams, mussels, oysters, cockles, scallops, geoducks, etc. — that have been recreationally or subsistence harvested. It does not apply to commercially harvested shellfish, which are tested before they enter the market. The advisory does not apply to other shellfish, such as crabs or shrimp, which do not carry PSP (unless you eat the crab butter/viscera).
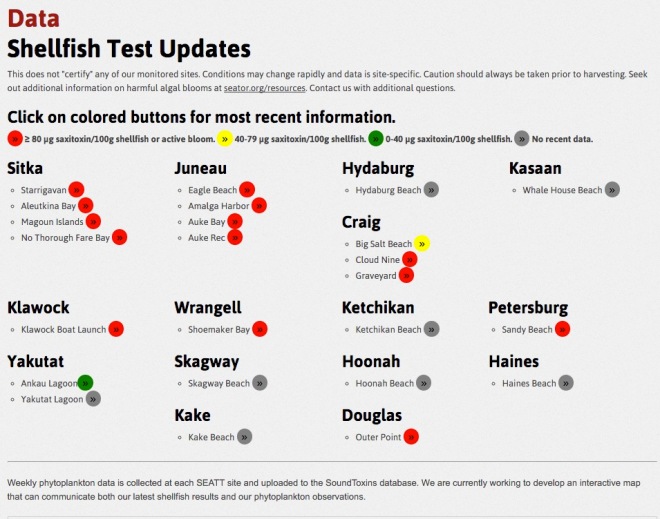
According to a SEATOR press release, “Recent samples on June 6 confirmed elevated levels of Alexandrium, the phytoplankton species that produces saxtoxins causing PSP, have been observed at the following locations and shellfish from these sites should not be harvested at this time.” The affected beaches from June 6 are Auke Bay, Amalga Harbor, Eagle Beach, and Auke Rec beaches in Juneau; Cloud 9 and Graveyard beaches in Craig; Starrigavan beach in Sitka; and the Boat Ramp beach in Klawock.

The butter clam has one set of rings that go one direction only, around the same center point (Photo courtesy of Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation)
In addition, the press release said, “On June 9 shellfish from the following sites tested above the regulatory limit of 80µg/100g for saxitoxins and should not be harvested at this time.” The June 9 list of beaches includes Sandy Beach in Petersburg (butter clams only); Auke Bay, Amalga Harbor, Eagle Beach, and Auke Rec beaches in Juneau; Aleutkina Bay, No Through Fare Bay, Magoun Islands, and Starrigavan (butter clams only) beaches in Sitka; and the Boat Ramp beach in Klawock. The advisory is for all shellfish on all beaches, except where noted.
According to SEATOR, “This does not ‘certify’ any of our monitored sites. Conditions may change rapidly and data is site-specific. Caution should always be taken prior to harvesting.”
SEATOR posts updates and information to its website at seator.org/data, which can help provide Southeast Alaska residents with reliable information so they can choose whether or not to harvest shellfish. In addition to testing water samples weekly from certain Southeast beaches, STAERL also tests samples of butter clams, littleneck clams, and blue mussels (which is STAERL’s indicator species because of how quickly blue mussels absorb saxotoxins).
Since most beaches in Alaska aren’t tested for harmful algal blooms, SEATOR and the SEATT partnership were formed in October 2014 to train people to test beaches in Southeast Alaska. In April 2015, the Sitka Tribe of Alaska opened a regional lab on Katlian Street, so samples could be tested in Sitka without having to be sent to the Lower 48, which delayed results. By testing for harmful algal blooms, SEATOR and the SEATT partnership hope to be able to provide information so people can make informed choices whether or not to harvest or eat shellfish.
Harmful algal blooms, such as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP), typically have not been monitored in Southeast Alaska for subsistence and recreational harvesters of clams, mussels, oysters, cockles, and other bivalves (commercial harvests are tested). Even though many people in Southeast Alaska love to harvest shellfish, eating it comes with some risks. There have been several PSP outbreaks in recent years that sent people to the hospital, and in 2010 two deaths were attributed to PSP and other HABs, such as Alexandrium, Pseudo-nitzchia and Dinophysis.
To learn more about harmful algal blooms and how they can raise the risk for PSP and ASP (amnesic shellfish poisoning, which also can be fatal), go to SEATOR’s resources page. If you have shellfish you recently harvested and want to test it, click this link to learn what you need to do to have it tested by STAERL. Please contact STAERL at 747-7395 with any additional questions.
• June 10, 2016, press release about PSP advisory for Southeast Alaska

















You must be logged in to post a comment.